临近入职,最近mt安排我看一点有关UE4中植被编辑的源码。而植被系统与地形系统又密切相关,因此本人决定一并阅读地形系统以源代码,并将阅读过程中整理出来的信息写成文档(可以显得我这几天干活比较卖力)。本文作为系列的第一篇文章,记录了地形编辑系统基本操作、源码结构;并以Sculpture功能为例,展示了编辑过程中的数据流通过程。
1. 地编系统的基本操作 在UE4中地形的编辑需要在landscape模式下进行。由于我UE的布局和网上大多数教程不一样,并没有Place Actor界面上的Landscape按钮,因此我一般是通过如图所示的modes按钮开启Landscape模式。
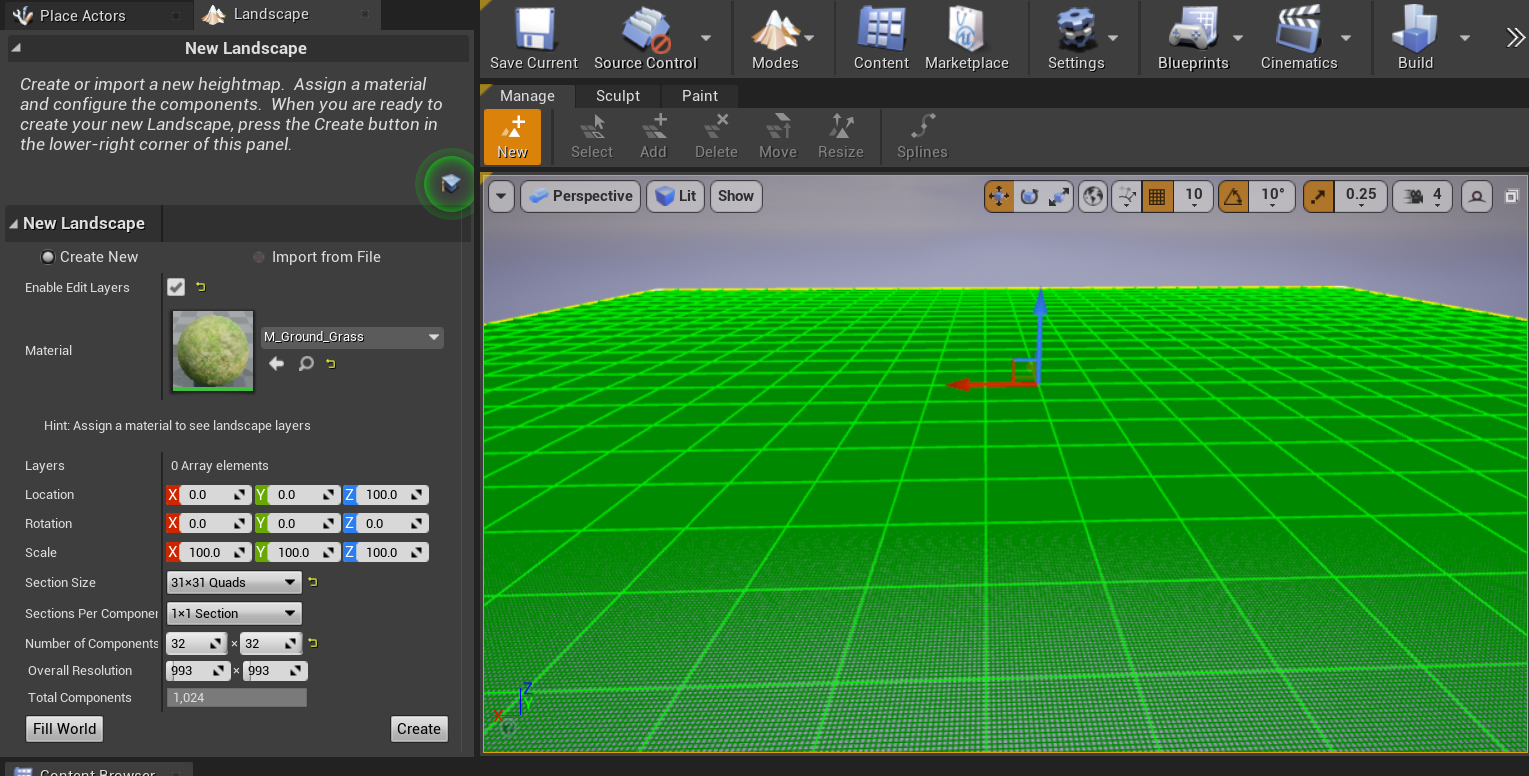
在第一次进入Landscape模式,没有创建任何Landscape的情况下,往往需要创建一个新的landscape。Landscape的创建界面如下图所示。
可以看到,一个地形对象的mesh被分为3个层级component-section-quad。其中,一个component可以包含多个section而一个section又可以包含多个quad,而一个quad为两个三角形拼成的方形,为构成地形对象的最小单位。
通过mesh确定了顶点的数量以及位置后,可以通过引入外部灰度图来初始化顶点的高度。通过New Landscape下的Import From File选项,可以从外部导入一个灰度图用于更新各个component的高度图。
除此以外,地形队形可以通过不同的material来改变其外观。在Material中,可以通过Landscape Layer Blend节点,为地形添加多个Layer以表现不同地形。
创建好地形后,可以看到引擎提供了三类操作对地形进行编辑:Sculpt、Paint以及Manage。
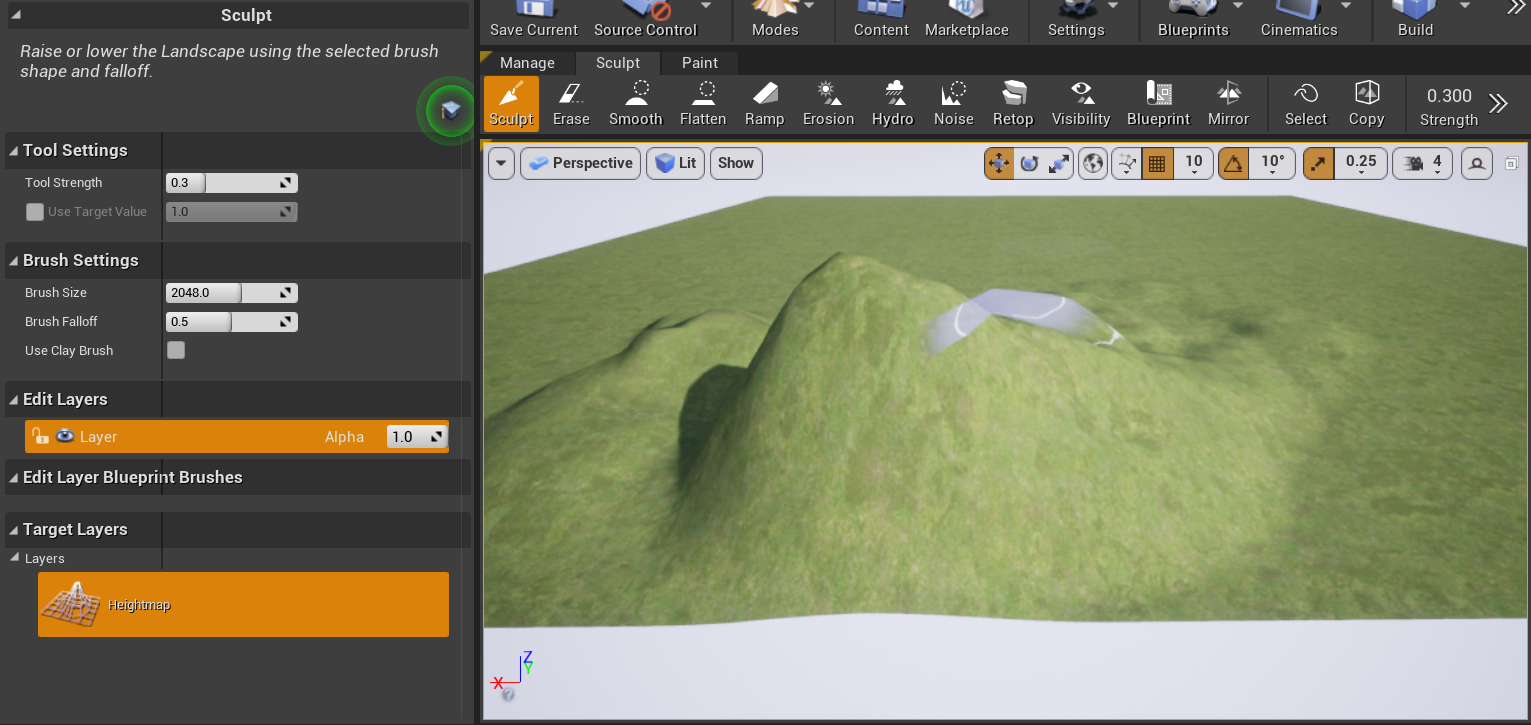
其中,Sculpt工具可以改变顶点的高度。选择Sculpt工具后,UE编辑器会在场景中生成一个可在场景中移动的笔刷。按住鼠标左键并移动可以使笔刷绘制到对应位置的高度图上,从而影响对应顶点的高度。
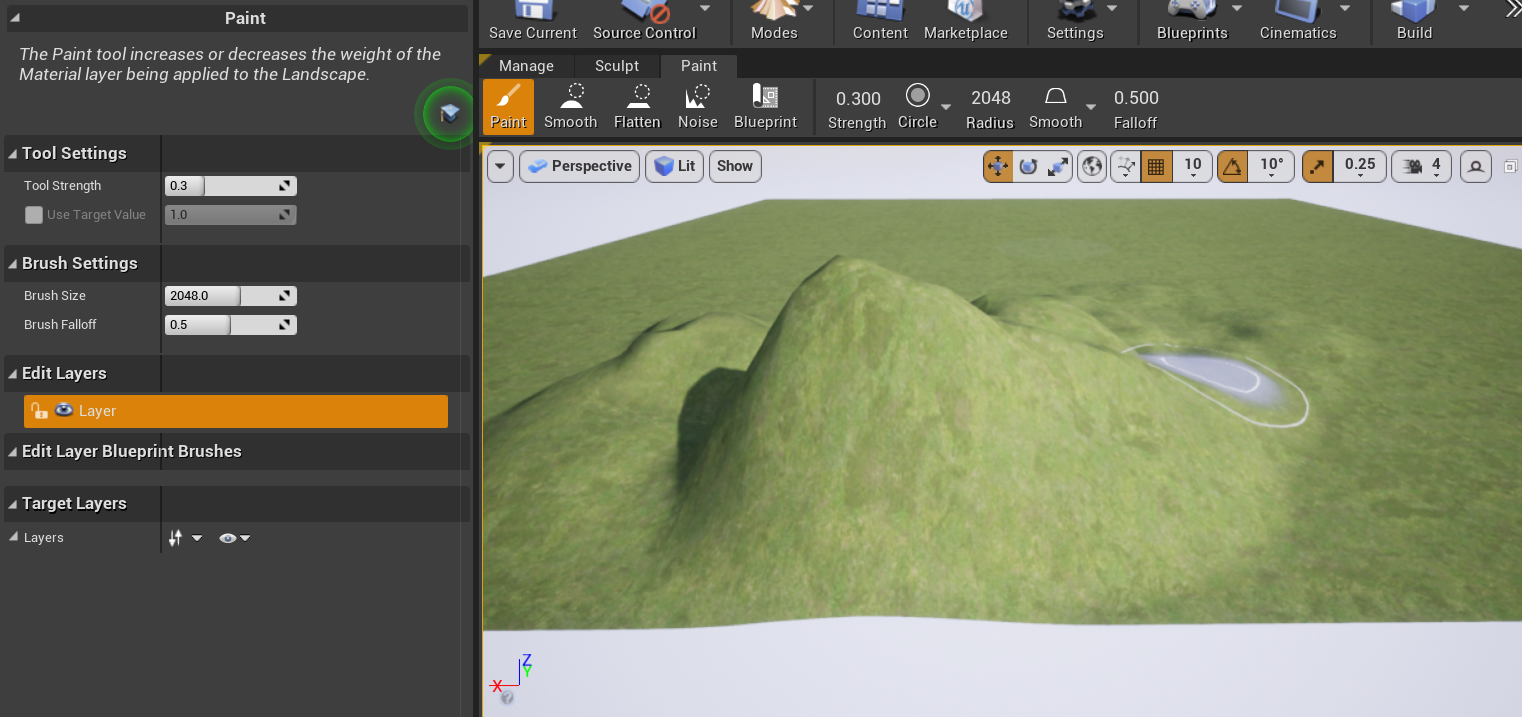
而Paint工具可以使用笔刷绘制到权重图上,以改变对应位置不同Layer之间的权重系数,使地形出现不同的外观表现。
Manage工具可以实现Landscape Component的增,删以及选中。若整个地形对象只有部分Component选中,则对地形的修改只会应用到被选中的Component上。值得一提的是,我们最开始的创建地形步骤同样属于一个Manage工具。
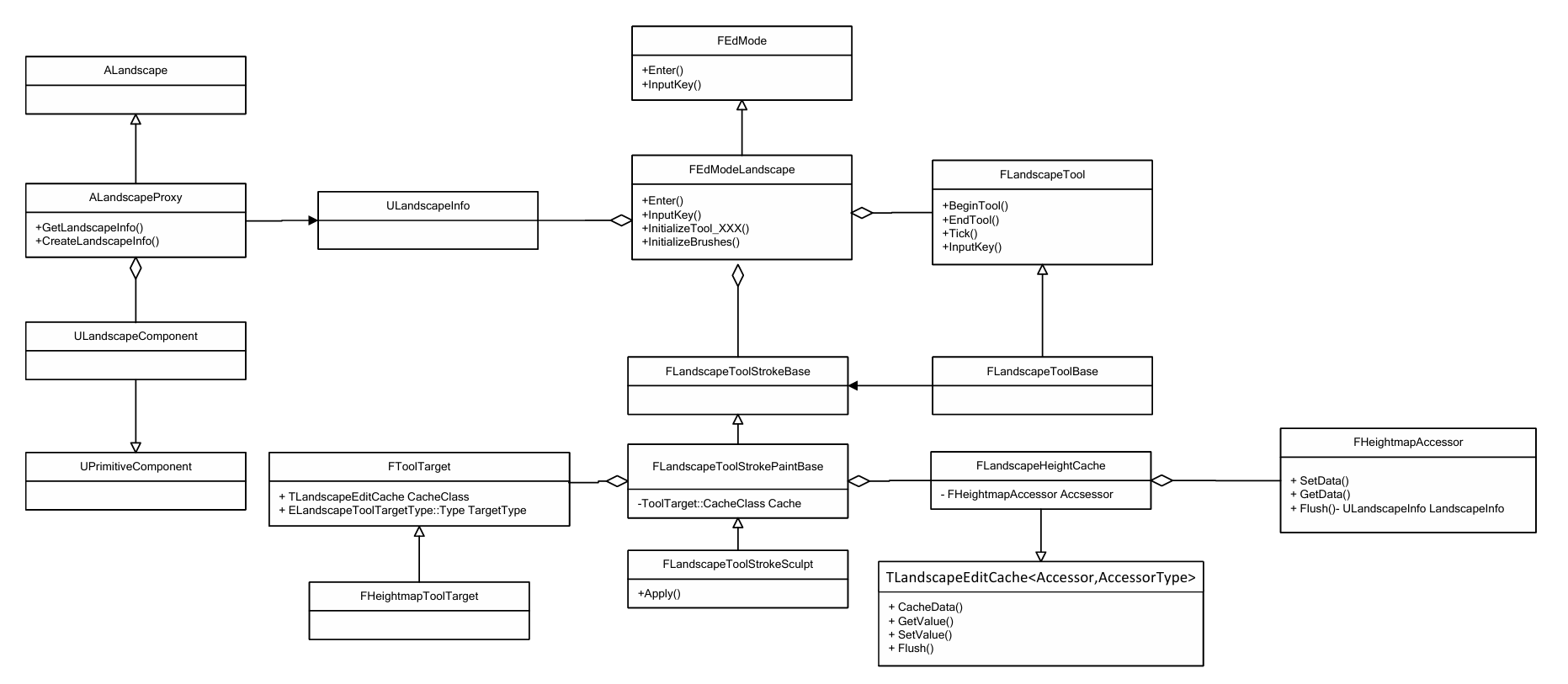
2. 地编系统的源码结构 以UE4.27的Sculpt工具为例,其地编系统不同类型的UML图如下图所示。
总的来说,这些类依据功能分为数据存储(ULandscapeComponent等)、输入输出处理(FEdModeLandscape、FLandscapeTool 等)以及数据更新(FLandscapeToolStrokeBase、FLandscapeHeightCache 等),其可以视作分别对应MVC结构中的Model, View以及Control三个部分。
下面将依据MVC的分类具体介绍不同类型的作用。
Model:
ALandscape / ALandscapeProxy: 对应可以放置在场景中的Actor,其主要由一系列ULandscapeComponent构成。对于外部类主要通过ALandscapeProxy 提供的结构与地形系统中的数据交互。ULandscapeComponent : 对应组成大地形的Component。各个Component中存储了具体的位置信息、顶点数据以及材质信息。同时,由于ULandscapeComponent 继承了UPrimitiveCompnent , 地形系统的渲染数据也由该Component提交。ULandscapeInfo : 在地形编辑系统中,一般通过ULandscapeInfo 对象访问并修改Component中的数据。ULandscapeComponent对象可以通过调用ALandscapeProxy的GetLandscapeInfo() 接口获取,并保存在FEdModeLandscape 对象中,并由FEdModeLandscape 分发给不同的对象编辑。
View:
FEdModeLandscape : 对应UE的Landscape模式。该对象负责处理用户的输入并管理地形编辑工具FLandscapeTool的状态切换。当用户输入事件生成时(如用户点击鼠标左键),编辑器会调用FEdModeLandscape的InputKey接口实现具体的处理逻辑。FLandscapeTool/FLandscapeToolBase : FLandscapeTool 实现了各个Landscape工具的具体逻辑。FEdModeLandscape可以调用FLandscapeTool 的BeginTool() 、EndTool()以及InputKey() 等接口实现Landscape工具的状态切换以及事件处理。而FLandscapeToolBase 在FLandscapeTool 的基础上实现了地形绘制类工具的逻辑。其可以通过指定笔刷实现在地形上的任意绘制。
Control:
FLandscapeToolStroke/FLandScapeToolStrokePaintBase : 对应不同的笔刷类型,负责更新后数据的计算以及更新操作。对于Paint类型的笔刷,通过FToolTarget指定的Data Cache对象来更新数据。这里FToolTarget并不是真实存在的类,而是FLandScapeToolStrokePaintBase 的模板参数,其定义了笔刷类目标对象的数据存储形式是什么(如FToolTarget 可以被指定为FHeightmapToolTarget 来实现对地形高度图的编辑)。由于这里使用了类似type trait的技巧实现了FToolTarget 的编译期多态,因此在UML图中使用了继承结构表现不同类之间的关系。而对于绘图类型的笔刷,可以通过调用Apply接口实现具体数据的计算以及更新。在FLandscapeToolBase 中,该工具在BeginTool() 以及Tick()函数中调用了Apply 接口实现笔刷在地图上的绘制(个人感觉这部分代码过于依赖模板了导致看起来很奇怪)。TLandscapeEditCache/FLandscapeHeightCache :控制笔刷传输过来的数据更新。由于Component的数据存储在UTexture2D*中,其更新可能涉及CPU以及GPU之间的数据通信,且可能涉及数据存储不连续的问题(笔刷更新的区域跨越了不同的Component)。因此,UE在Component以及Stroke对象之间设计了Cache对象将需要更新的数据缓存下来,待Stroke更新的数据写入结束后一次性将更新的数据输出到Component中。FHeightmapAccessor : Accessor对象负责将数据更新到Component中。其内部保存了由FEdModeLandscape 对象传入的ULandscapeInfo 指针,并通过ULandscapeInfo 计算需要更新的Component以及对应的UTexture2D。随后将Cache对象传入的数据写入到对应Component中实现数据更新。
3.地编系统中的数据流 下面我们将以Sculpt工具为例,刨析从用户鼠标点击事件开始到画面中顶点高度更新结束,数据在地形编辑系统中的流通过程。注意,由于本文只专注地形编辑系统的总体结构,因此不对任何具体算法做任何解析。
在刚进入Landscape Mode时,Landscape Editor Mode会通过当前选中的Landscape Proxy获取对应的Landscape Info,并通过调用SetLandscapeInfo 更新CurrentToolTarget的LandscapeInfo信息。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 void FEdModeLandscape::Enter () ... ALandscapeProxy* SelectedLandscape = GEditor->GetSelectedActors ()->GetTop <ALandscapeProxy>(); if (SelectedLandscape) { SetLandscapeInfo (SelectedLandscape->GetLandscapeInfo ()); GEditor->SelectNone (false , true ); GEditor->SelectActor (SelectedLandscape, true , false ); } else { GEditor->SelectNone (true , true ); } ... } void FEdModeLandscape::SetLandscapeInfo (ULandscapeInfo* InLandscapeInfo) if (CurrentToolTarget.LandscapeInfo != InLandscapeInfo) { { TGuardValue<bool > GuardFlag (bUpdatingLandscapeInfo, true ) ; CurrentToolTarget.LandscapeInfo = InLandscapeInfo; ... } ... } }
随后当UE检测到用户的输入事件时(如鼠标点击左键),会调用InputKey函数处理,如下面这段代码片段所示。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 bool FEdModeLandscape::InputKey (FEditorViewportClient* ViewportClient, FViewport* Viewport, FKey Key, EInputEvent Event) ... if (NewLandscapePreviewMode != ENewLandscapePreviewMode::None) { ... } else { ... if (CurrentTool && CurrentTool->InputKey (ViewportClient, Viewport, Key, Event) == true ) { return true ; } ... if (Key == EKeys::LeftMouseButton && Event == IE_Pressed) { ... bool bMovingCamera = Viewport->KeyState (EKeys::MiddleMouseButton) || Viewport->KeyState (EKeys::RightMouseButton) || IsAltDown (Viewport); if ((Viewport->IsPenActive () && Viewport->GetTabletPressure () > 0.0f ) || (!bMovingCamera && ViewportClient->GetCurrentWidgetAxis () == EAxisList::None && ((LandscapeEditorControlType == ELandscapeFoliageEditorControlType::IgnoreCtrl) || (LandscapeEditorControlType == ELandscapeFoliageEditorControlType::RequireCtrl && IsCtrlDown (Viewport)) || (LandscapeEditorControlType == ELandscapeFoliageEditorControlType::RequireNoCtrl && !IsCtrlDown (Viewport))))) { if (CurrentTool && (CurrentTool->GetSupportedTargetTypes () == ELandscapeToolTargetTypeMask::NA || CurrentToolTarget.TargetType != ELandscapeToolTargetType::Invalid)) { FVector HitLocation; if (LandscapeMouseTrace (ViewportClient, HitLocation)) { ... if (CurrentTool->CanToolBeActivated ()) { bool bToolActive = CurrentTool->BeginTool (ViewportClient, CurrentToolTarget, HitLocation); if (bToolActive) { ToolActiveViewport = Viewport; } else { ToolActiveViewport = nullptr ; Viewport->CaptureMouse (false ); } ViewportClient->Invalidate (false , false ); return bToolActive; } } } return true ; } } if (Key == EKeys::LeftMouseButton || (LandscapeEditorControlType == ELandscapeFoliageEditorControlType::RequireCtrl && (Key == EKeys::LeftControl || Key == EKeys::RightControl))) { if (Event == IE_Released && CurrentTool && CurrentTool->IsToolActive () && ToolActiveViewport) { Viewport->SetPreCaptureMousePosFromSlateCursor (); CurrentTool->EndTool (ViewportClient); Viewport->CaptureMouse (false ); ToolActiveViewport = nullptr ; return true ; } } ... } return false ; }
可以看到,在InputKey中,主要检测了两类事件:用户按下鼠标左键以及用户松开鼠标左键。在用户按下左键并检查通过一系列状态设置后,Landscape Editor会调用当前选中的Landscape工具的BeginTool将工具切换为激活状态。而在用户松开左键时,Landscape Editor则会调用EndTool 结束工具的激活状态。
以Sculpt工具为例,其BeginTool,Tick以及EndTool的定义如下片段所示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 virtual bool BeginTool (FEditorViewportClient* ViewportClient, const FLandscapeToolTarget& InTarget, const FVector& InHitLocation) override ... if ( !IsToolActive () ) { ToolStroke.Emplace ( EdMode, ViewportClient, InTarget ); EdMode->CurrentBrush->BeginStroke ( InHitLocation.X, InHitLocation.Y, this ); } LastInteractorPosition = FVector2D (InHitLocation); InteractorPositions.Emplace (LastInteractorPosition, ViewportClient ? IsModifierPressed (ViewportClient) : false ); TimeSinceLastInteractorMove = 0.0f ; ToolStroke->Apply (ViewportClient, EdMode->CurrentBrush, EdMode->UISettings, InteractorPositions); ... return true ; } virtual void Tick (FEditorViewportClient* ViewportClient, float DeltaTime) override if (IsToolActive ()) { if (InteractorPositions.Num () > 0 ) { ToolStroke->Apply (ViewportClient, EdMode->CurrentBrush, EdMode->UISettings, InteractorPositions); ViewportClient->Invalidate (false , false ); InteractorPositions.Empty (1 ); } else if (TStrokeClass::UseContinuousApply && TimeSinceLastInteractorMove >= 0.25f ) { InteractorPositions.Emplace (LastInteractorPosition, IsModifierPressed (ViewportClient)); ToolStroke->Apply (ViewportClient, EdMode->CurrentBrush, EdMode->UISettings, InteractorPositions); ViewportClient->Invalidate (false , false ); InteractorPositions.Empty (1 ); } TimeSinceLastInteractorMove += DeltaTime; ... } } virtual void EndTool (FEditorViewportClient* ViewportClient) override if (IsToolActive () && InteractorPositions.Num ()) { ToolStroke->Apply (ViewportClient, EdMode->CurrentBrush, EdMode->UISettings, InteractorPositions); InteractorPositions.Empty (1 ); } ToolStroke.Reset (); EdMode->CurrentBrush->EndStroke (); ... } virtual bool MouseMove (FEditorViewportClient* ViewportClient, FViewport* Viewport, int32 x, int32 y) override if (ViewportClient != nullptr && Viewport != nullptr ) { FVector HitLocation; if (EdMode->LandscapeMouseTrace (ViewportClient, x, y, HitLocation)) { if (EdMode->CurrentBrush && !EdMode->IsAdjustingBrush (Viewport)) { EdMode->CurrentBrush->MouseMove (HitLocation.X, HitLocation.Y); } if (IsToolActive ()) { if (InteractorPositions.Num () == 0 || LastInteractorPosition != FVector2D (HitLocation)) { LastInteractorPosition = FVector2D (HitLocation); InteractorPositions.Emplace (LastInteractorPosition, IsModifierPressed (ViewportClient)); } TimeSinceLastInteractorMove = 0.0f ; } } } else { const FVector2D NewPosition (x, y); if (InteractorPositions.Num () == 0 || LastInteractorPosition != FVector2D (NewPosition)) { LastInteractorPosition = FVector2D (NewPosition); InteractorPositions.Emplace (LastInteractorPosition, IsModifierPressed ()); } TimeSinceLastInteractorMove = 0.0f ; } return true ; }
可以看到,在Sculpt Tool激活的状态下,会收集当前鼠标的位置记录在InterationPositions数组中,并调用笔刷对象的Apply函数更新地形内容。
Sculpt工具使用的笔刷为FLandscapeToolStrokeSculpt ,其Apply的实现如下所示。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 void Apply (FEditorViewportClient* ViewportClient, FLandscapeBrush* Brush, const ULandscapeEditorObject* UISettings, const TArray<FLandscapeToolInteractorPosition>& InteractorPositions) ... int32 X1, Y1, X2, Y2; BrushInfo.GetInclusiveBounds (X1, Y1, X2, Y2); ... X1 -= 1 ; Y1 -= 1 ; X2 += 1 ; Y2 += 1 ; ... this ->Cache.CacheData (X1, Y1, X2, Y2); TArray<ToolTarget::CacheClass::DataType> Data; this ->Cache.GetCachedData (X1, Y1, X2, Y2, Data); ... this ->Cache.SetCachedData (X1, Y1, X2, Y2, Data); this ->Cache.Flush (); }
在FLandscapeToolStrokeSculpt 中,首先根据BrushInfo计算当前笔刷对应的地形区域范围,接着利用Cache::CacheData 将数据读取到内存中。随后,经过计算,将更新后的数据写回到Cache中并Flush到Component中。
FLandscapeToolStrokeSculpt 使用的Cache类型为FLandscapeHeightCache, 其CacheData,SetCacheData以及Flush的实现为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 void CacheData (int32 X1, int32 Y1, int32 X2, int32 Y2, bool bCacheOriginalData = false ) if (!Valid) { if (Accessor::bUseInterp) { ValidX1 = CachedX1 = X1; ValidY1 = CachedY1 = Y1; ValidX2 = CachedX2 = X2; ValidY2 = CachedY2 = Y2; DataAccess.GetData (ValidX1, ValidY1, ValidX2, ValidY2, CachedData); if (!ensureMsgf (ValidX1 <= ValidX2 && ValidY1 <= ValidY2, TEXT ("Invalid cache area: X(%d-%d), Y(%d-%d) from region X(%d-%d), Y(%d-%d)" ), ValidX1, ValidX2, ValidY1, ValidY2, X1, X2, Y1, Y2)) { Valid = false ; return ; } } ... Valid = true ; } else { ... } } void SetCachedData (int32 X1, int32 Y1, int32 X2, int32 Y2, TArray<AccessorType>& Data, ELandscapeLayerPaintingRestriction PaintingRestriction = ELandscapeLayerPaintingRestriction::None, bool bUpdateData = true ){ checkSlow (Data.Num () == (1 + Y2 - Y1) * (1 + X2 - X1)); for (int32 Y = Y1; Y <= Y2; Y++) { for (int32 X = X1; X <= X2; X++) { SetValue (X, Y, Data[(X - X1) + (Y - Y1)*(1 + X2 - X1)]); } } if (bUpdateData) { DataAccess.SetData (X1, Y1, X2, Y2, Data.GetData (), PaintingRestriction); } } void Flush () DataAccess.Flush (); }
可以看到,CacheData 通过Accessor 获取对应区域的数据并缓存到本地数组CachedData中。而用户可以通过SetCachedData 更新本地的CachedData 数组。最后,用户需要调用Flush 使Accessor更新数据。
FHeightmapAccessor 的SetData以及Flush接口的实现如下所示。可以看到,FHeightmapAccessor的SetData以及Flush接口均由FLandscapeEditDataInterface 类型的对象LandscapeEdit 间接完成。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 void SetData (int32 X1, int32 Y1, int32 X2, int32 Y2, const uint16* Data, ELandscapeLayerPaintingRestriction PaintingRestriction = ELandscapeLayerPaintingRestriction::None) TSet<ULandscapeComponent*> Components; if (LandscapeInfo && LandscapeEdit->GetComponentsInRegion (X1, Y1, X2, Y2, &Components)) { ChangedComponents.Append (Components); for (ULandscapeComponent* Component : Components) { Component->RequestHeightmapUpdate (); } bool bUpdateFoliage = false ; bool bUpdateNormals = false ; ... if (bUpdateFoliage) { ... } else { LandscapeEdit->SetHeightData (X1, Y1, X2, Y2, Data, 0 , bUpdateNormals); } } } void Flush () LandscapeEdit->Flush (); }
FLandscapeEditDataInterface 在Accessor内部由Edit Mode传入的ULandscapeInfo 构造,其负责具体的数据更新的逻辑。其SetHeightData接口以及Flush接口的实现如下所示。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 void FLandscapeEditDataInterface::SetHeightData (int32 X1, int32 Y1, int32 X2, int32 Y2, const uint16* InData, int32 InStride, bool InCalcNormals, const uint16* InNormalData, const uint16* InHeightAlphaBlendData, const uint8* InHeightFlagsData, bool InCreateComponents, UTexture2D* InHeightmap, UTexture2D* InXYOffsetmapTexture, bool InUpdateBounds, bool InUpdateCollision, bool InGenerateMips) const int32 NumVertsX = 1 + X2 - X1; const int32 NumVertsY = 1 + Y2 - Y1; if (InStride == 0 ) { InStride = NumVertsX; } check (ComponentSizeQuads > 0 ); int32 ComponentIndexX1, ComponentIndexY1, ComponentIndexX2, ComponentIndexY2; ALandscape::CalcComponentIndicesOverlap (X1, Y1, X2, Y2, ComponentSizeQuads, ComponentIndexX1, ComponentIndexY1, ComponentIndexX2, ComponentIndexY2); FVector* VertexNormals = nullptr ; if (InCalcNormals) { ... } for (int32 ComponentIndexY = ComponentIndexY1; ComponentIndexY <= ComponentIndexY2; ComponentIndexY++) { for (int32 ComponentIndexX = ComponentIndexX1; ComponentIndexX <= ComponentIndexX2; ComponentIndexX++) { FIntPoint ComponentKey (ComponentIndexX, ComponentIndexY) ; ULandscapeComponent* Component = LandscapeInfo->XYtoComponentMap.FindRef (ComponentKey); ... UTexture2D* Heightmap = InHeightmap != nullptr ? InHeightmap : Component->GetHeightmap (true ); UTexture2D* XYOffsetmapTexture = InXYOffsetmapTexture != nullptr ? InXYOffsetmapTexture : Component->XYOffsetmapTexture; Component->Modify (GetShouldDirtyPackage ()); FLandscapeTextureDataInfo* TexDataInfo = GetTextureDataInfo (Heightmap); FColor* HeightmapTextureData = (FColor*)TexDataInfo->GetMipData (0 ); ... int32 SizeU = Heightmap->Source.GetSizeX (); int32 SizeV = Heightmap->Source.GetSizeY (); int32 HeightmapOffsetX = Component->HeightmapScaleBias.Z * (float )SizeU; int32 HeightmapOffsetY = Component->HeightmapScaleBias.W * (float )SizeV; int32 ComponentX1 = FMath::Clamp <int32>(X1 - ComponentIndexX*ComponentSizeQuads, 0 , ComponentSizeQuads); int32 ComponentY1 = FMath::Clamp <int32>(Y1 - ComponentIndexY*ComponentSizeQuads, 0 , ComponentSizeQuads); int32 ComponentX2 = FMath::Clamp <int32>(X2 - ComponentIndexX*ComponentSizeQuads, 0 , ComponentSizeQuads); int32 ComponentY2 = FMath::Clamp <int32>(Y2 - ComponentIndexY*ComponentSizeQuads, 0 , ComponentSizeQuads); int32 SubIndexX1 = FMath::Clamp <int32>((ComponentX1 - 1 ) / SubsectionSizeQuads, 0 , ComponentNumSubsections - 1 ); int32 SubIndexY1 = FMath::Clamp <int32>((ComponentY1 - 1 ) / SubsectionSizeQuads, 0 , ComponentNumSubsections - 1 ); int32 SubIndexX2 = FMath::Clamp <int32>(ComponentX2 / SubsectionSizeQuads, 0 , ComponentNumSubsections - 1 ); int32 SubIndexY2 = FMath::Clamp <int32>(ComponentY2 / SubsectionSizeQuads, 0 , ComponentNumSubsections - 1 ); uint16 MinHeight = MAX_uint16; uint16 MaxHeight = 0 ; for (int32 SubIndexY = SubIndexY1; SubIndexY <= SubIndexY2; SubIndexY++) { for (int32 SubIndexX = SubIndexX1; SubIndexX <= SubIndexX2; SubIndexX++) { ... int32 TexX1 = HeightmapOffsetX + (SubsectionSizeQuads + 1 ) * SubIndexX + SubX1; int32 TexY1 = HeightmapOffsetY + (SubsectionSizeQuads + 1 ) * SubIndexY + SubY1; int32 TexX2 = HeightmapOffsetX + (SubsectionSizeQuads + 1 ) * SubIndexX + SubX2; int32 TexY2 = HeightmapOffsetY + (SubsectionSizeQuads + 1 ) * SubIndexY + SubY2; TexDataInfo->AddMipUpdateRegion (0 , TexX1, TexY1, TexX2, TexY2); } } Component->RequestHeightmapUpdate (); ... FPlatformMisc::CreateGuid (Component->StateId); } } if (VertexNormals) { delete [] VertexNormals; } } x void FLandscapeTextureDataInterface::Flush () bool bNeedToWaitForUpdate = false ; if (bUploadTextureChangesToGPU) { for (TMap<UTexture2D*, FLandscapeTextureDataInfo*>::TIterator It (TextureDataMap); It; ++It) { if (It.Value ()->UpdateTextureData ()) { bNeedToWaitForUpdate = true ; } } } if ( bNeedToWaitForUpdate ) { FlushRenderingCommands (); } for ( TMap<UTexture2D*, FLandscapeTextureDataInfo*>::TIterator It (TextureDataMap); It; ++It ) { delete It.Value (); } TextureDataMap.Empty (); }
可以看到,在SetHeightData 中会计算更新区域覆盖Component的范围,并将数据写入到对应的height map的纹理缓冲区中。而在Flush 中会生成并执行更新纹理的渲染命令,并清空临时缓冲区,从而完成画面中地形顶点位置的更新。
4. 小结 本文从UE地编系统的基础操作出发,介绍了地编系统的代码结构以及地形数据更新的流程。由于本文目标旨在整体代码结构介绍,因此对于地形编辑系统的具体算法(顶点的更新算法、被影响植被位置的更新算法、地形的渲染等)未作讨论,这可能在后续的文章中详细展开。